dataset & model build
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import numpy as np
#device name
import tensorflow as tf
if tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'):
device_name=tf.test.gpu_device_name()
else:
device_name='/CPU:0'
mnist_bldr = tfds.builder('mnist')
mnist_bldr.download_and_prepare()
mnist = mnist_bldr.as_dataset(shuffle_files=False)
def preprocess(ex, mode='uniform'):
image = ex['image']
image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, tf.float32)
image = image*2 - 1.0
if mode == 'uniform':
input_z = tf.random.uniform(
shape=(z_size,), minval=-1.0, maxval=1.0)
elif mode == 'normal':
input_z = tf.random.normal(shape=(z_size,))
return input_z, image
num_epochs=100
batch_size=128
image_size=(28, 28)
z_size=20
mode_z='uniform'
lambda_gp=10.0
tf.random.set_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
mnist_trainset=mnist['train']
mnist_trainset=mnist_trainset.map(preprocess)
mnist_trainset=mnist_trainset.shuffle(10000)
mnist_trainset=mnist_trainset.batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True)
with tf.device(device_name):
gen_model=make_dcgan_generator()
gen_model.build(input_shape=(None, z_size))
disc_model=make_dcgan_discriminator()
disc_model.build(input_shape=(None, np.prod(image_size)))
train
일반적으로 WGAN에서는 RMSProp 옵티마이저가 권장된다.
반면 WGAN-GP에는 Adam 옵티마이저가 권장된다.
import time
g_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.0002)
d_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.0002)
if mode_z=='uniform':
fixed_z=tf.random.uniform(shape=(batch_size, z_size), minval=-1, maxval=1)
elif mode_z=='normal':
fixed_z=tf.random.uniform(shape=(batch_size, z_size))
def create_samples(g_model, input_z):
g_output=g_model(input_z, training=False)
images=tf.reshape(g_output, (batch_size, *image_size))
return (images+1)/2.0
all_losses=[]
epoch_samples=[]
start_time=time.time()
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs+1):
epoch_losses=[]
for i, (input_z, input_real) in enumerate(mnist_trainset):
with tf.GradientTape() as d_tape, tf.GradientTape() as g_tape:
g_output=gen_model(input_z, training=True)
d_critics_real=disc_model(input_real, training=True)
d_critics_fake=disc_model(g_output, training=True)
g_loss=-tf.math.reduce_mean(d_critics_fake)
d_loss_real=-tf.math.reduce_mean(d_critics_real)
d_loss_fake=tf.math.reduce_mean(d_critics_fake)
d_loss=d_loss_real+d_loss_fake
with tf.GradientTape() as gp_tape:
alpha=tf.random.uniform(shape=[d_critics_real.shape[0], 1, 1, 1], minval=0.0, maxval=1.0)
interpolated=(alpha*input_real+(1-alpha)*g_output)
gp_tape.watch(interpolated)
d_critics_intp=disc_model(interpolated)
grads_intp=gp_tape.gradient(d_critics_intp, [interpolated, ])[0]
grads_intp_l2=tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(grads_intp), axis=[1, 2, 3]))
grad_penalty=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(grads_intp_l2-1.0))
d_loss=d_loss+lambda_gp*grad_penalty
d_grads=d_tape.gradient(d_loss, disc_model.trainable_variables)
d_optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(d_grads, disc_model.trainable_variables))
g_grads=g_tape.gradient(g_loss, gen_model.trainable_variables)
g_optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(g_grads, gen_model.trainable_variables))
epoch_losses.append((g_loss.numpy(), d_loss.numpy(), d_loss_real.numpy(), d_loss_fake.numpy()))
all_losses.append(epoch_losses)
print('에포크 {:03d} | 시간 {:.2f} min | 평균 손실 >> 생성자/판별자 {:6.2f}/{:6.2f} [판별자-진짜: {:6.2f} 판별자-가짜: {:6.2f}]'.format(epoch, (time.time()-start_time)/60, *list(np.mean(all_losses[-1], axis=0))))
epoch_samples.append(create_samples(gen_model, fixed_z).numpy())
Graph
import itertools
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
ax=fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
g_losses=[item[0] for item in itertools.chain(*all_losses)]
d_losses=[item[1] for item in itertools.chain(*all_losses)]
plt.plot(g_losses, label='Generator loss', alpha=0.95)
plt.plot(d_losses, label='Discriminator loss', alpha=0.95)
plt.legend(fontsize=20)
ax.set_xlabel('Iteration', size=15)
ax.set_ylabel('Loss', size=15)
epochs=np.arange(1, 101)
epoch2iter=lambda e: e*len(all_losses[-1])
epoch_ticks=[1, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100]
newpos=[epoch2iter(e) for e in epoch_ticks]
ax2=ax.twiny()
ax2.set_xticks(newpos)
ax2.set_xticklabels(epoch_ticks)
ax2.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax2.xaxis.set_label_position('bottom')
ax2.spines['bottom'].set_position(('outward', 60))
ax2.set_xlabel('Epoch', size=15)
ax2.set_xlim(ax.get_xlim())
ax.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=15)
ax2.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=15)
plt.show()
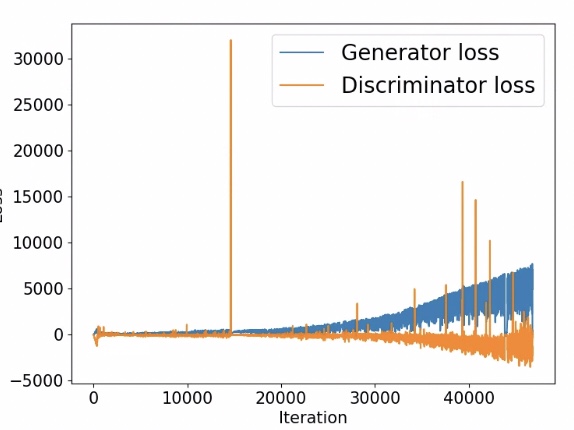 ???
???from epoch_sampels get images
selected_epochs=[1, 2, 4, 10, 50, 100]
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(10, 14))
for i, e in enumerate(selected_epochs):
for j in range(5):
ax=fig.add_subplot(6, 5, i*5+j+1)
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
if j==0:
ax.text(-0.06, 0.5, 'Epoch {}'.format(e), rotation=90, size=18, color='red', horizontalalignment='right', verticalalignment='center', transform=ax.transAxes)
image=epoch_samples[e-1][j]
ax.imshow(image, cmap='gray_r')
plt.show()
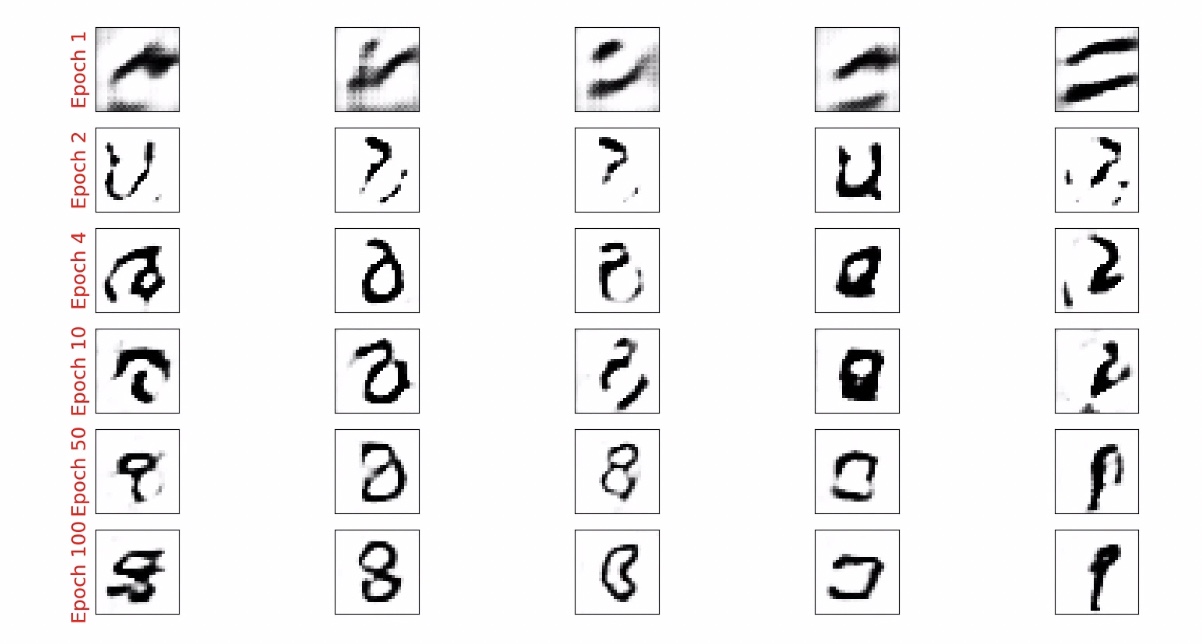
바닐라 GAN에서의 생성된 샘플보다 DCGAN이 훨씬 높은 품질을 가진 이미지를 생성함을 알 수 있다.